Treatments
Home / Treatments / Peels

What is chemical peeling?
Chemical Peeling is exactly what it says – peeling of the skin using a chemical. A chemical peel removes the outer layers of the skin. This freshens the skin, removes sunspots and rough scaly patches, and reduces freckles, fine wrinkles, and irregular pigmentation. It is safest and most effective on the face.
There are many types of peels available. In general, Glycolic peels are the lightest, then Jessner peels, and finally, TCA peels, in order of increasing strength.
How does it work?
The solution is applied to the skin, causing a mild acid burn to the top layers, i.e. those layers that are most sun-damaged. As these layers peel off over a week or so, new, fresh, unblemished skin forms from the deeper layers. Peeling stimulates the growth of healthy new skin cells in place of tired old sun-damaged skin.
This process is to be sharply contrasted with sunburn, which removes the outer layers of skin, but causes UV damage to deeper cells, thereby accelerating the ageing process and the risk of skin cancer.
What conditions can be treated with peels?
Fine wrinkling can be reduced with chemical peeling. Most brown marks, freckles and pigmentation can also be removed or lessened, especially age and liver spots.
Scaly patches and rough skin (keratoses) can be removed. Very thick keratoses may need additional treatments for complete removal.
Acne and acne scarring can also be reduced with peels.
What are the risks of peels?
Pigment changes can be caused by a peel in people prone to this complication due to their skin type. Those known to develop brown discoloration after injury such as a mild burn should have a test area peeled first before undergoing a full chemical peel.
Any increased pigmentation usually resolves with time. It can be largely prevented by strict use of sunscreen for three months after the peel, and skin preparation before the peel with special creams and serums.
Cold sores can be activated in those prone to this kind of condition. Anti-viral medication can prevent this.
Scarring can occur with strong peels, but is unusual with weaker ones. The most common causes of scarring are infection, and picking off the skin before it is ready to peel. Both of these are avoidable.
What is the procedure?
The skin may have had preparation with Vitamin A, Alpha Hydroxy Acid (AHA) or other preparations.
Firstly, the skin is thoroughly cleansed. The solution is then applied to the face and monitored.
If burning or stinging is a problem, a cold pack or fan may be helpful. Often the treatment is carried out in sections.
What happens afterwards?
The skin will go red over the first 24 hours. Once the initial burning has worn off it is not painful, but feels tight. Over the next few days, the skin dries and looks like brownish leather.
Vaseline should be applied several times a day to prevent cracking. Water will do no harm but soap should be avoided.
The skin will begin to peel between 3 and 7 days later, and must be left to come off at its own pace.
As soon as the skin has healed, make-up may be applied over any new, pink skin. Sometimes a secondary peel occurs during the second week in the form of dry, scaling skin. Sunscreen is mandatory for at least three months, and plain moisturisers, such as sorbolenne, are helpful.
Additionally, the use of certain creams and serums can continue to improve the skin texture and reverse some of the effects caused by years of sun exposure.
Lactic Peels
Lactic acid is an Alpha-Hydroxy Acid (AHA) derived from milk, which is combined with Canadian Willowherb (an anti inflammatory) to create a unique minimal downtime peel. This targets the epidermis (the uppermost layer of the skin), breaking down the glue that holds the skin cells together. This enables a faster cell turn-over, resulting in a more youthful appearance to the skin as the healthier layers of skin are brought to the surface.
Lactobotanical peels are suitable for most skin types, and results can be noticed for epidermal hyperpigmentation, sun damage, mild acne, congestion, dull or lifeless skin and dehydration.
Lactobotanical peels have a pH of 2.9-3.15, with lactic acid concentrations of 20%, 30%, 40% and 60%. We begin with the 20% strength peel and increase it every 2 weeks according to your skin’s response.
Salicylic Peels
Salicylic Acid (derived from the bark of certain trees) is a Beta Hydroxy Acid (BHA) peel. It works on the deeper layers of the skin, and is more intensive than a peel you would receive in a beauty salon. Salicylic Acid peels are especially good for treating acne.
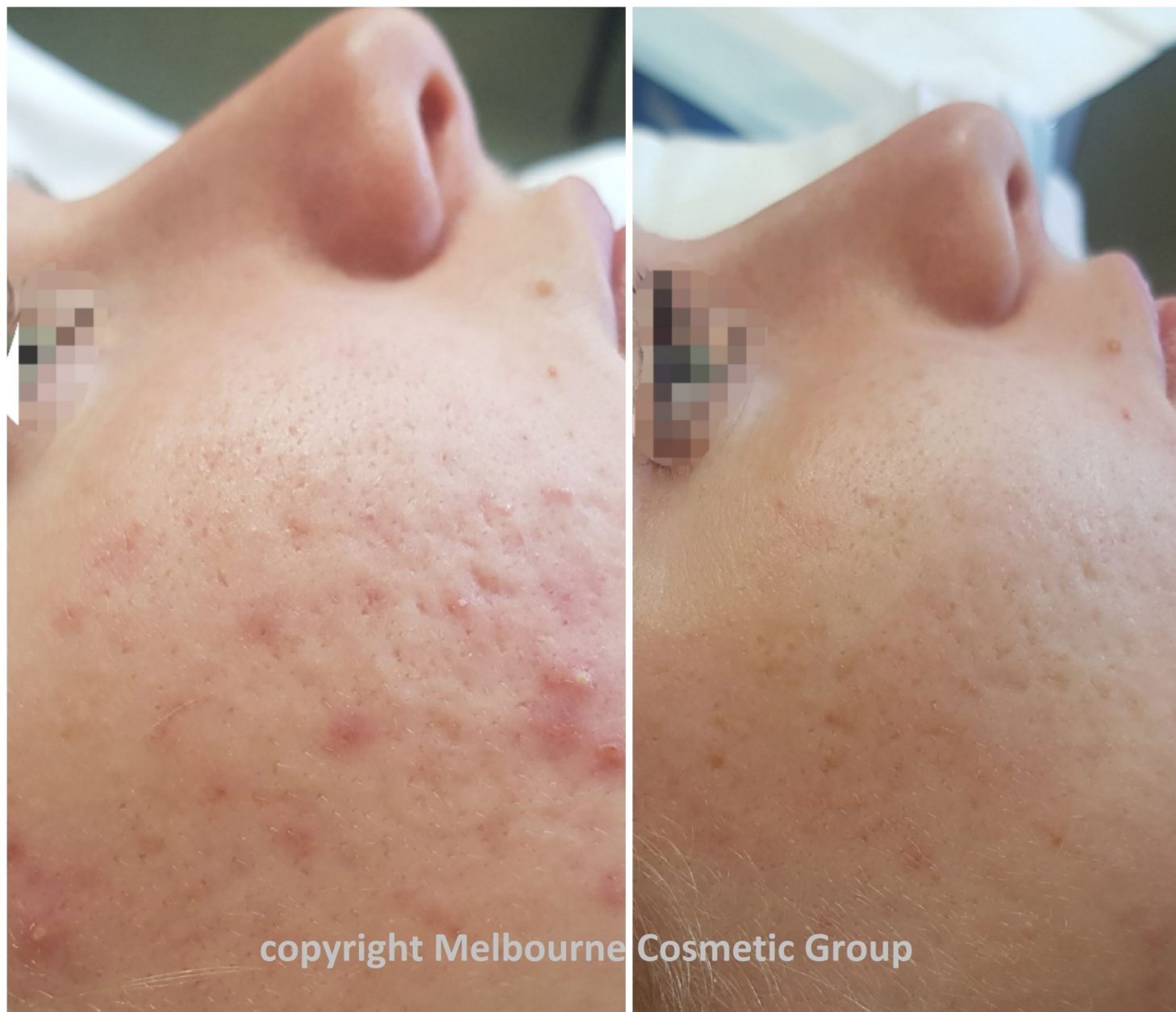
BHA peels work on the same principal as an AHA peel, breaking down the glue between the skin cells, but at a much deeper level. As it has its own natural anti-inflammatory agents, it can be less irritating to the skin.
Salicylic peels are layered on to the skin, beginning with one layer the first treatment, and then adding subsequent layers every 4 weeks according to your skin’s response.
If you would like to learn more about medical peels, please make an appointment for a free consultation with our qualified and experienced staff, who can discuss your cosmetic options, goals and expectations with you to determine the type of treatment that would benefit you most.
Anti Wrinkle Injections
Dermal Fillers for Wrinkles
Lip Enhancement
Anti-Wrinkle Laser
Dermapen 4 Skin Needling
Blood Vessel Laser
Tattoo Removal Laser
IPL Photo Rejuvenation
SHR IPL Hair Reduction
LED Photo Rejuvenation
Mole Max
Ultrasound Fat Lipolysis
Skin Tightening
MicroSclerotherapy
MicroDermabrasion
Intraceuticals Oxygen Infusions
Carbon Facials
Peels
Permanent Makeup







